If you have a question, we probably have an answer. But if you can't find it here, contact us!
FAQs
CONTACT USANSI and AQL
Acceptable Quality Level.
The acceptable level (AQL) is defined as the maximum percent defective (or the maximum number of defects per hundred units) that, for purpose of sampling inspection, can be considered satisfactory as a process average.The largest quantity of defectives in a certain sample size can make the lot definitely acceptable or rejected.
About Reports
1. What is an evaluation, and what does it generally include?
Evaluation means identifying problems or shortcomings in the management system that could allow poor quality products to be produced and bringing it to the attention of management so they can correct the problem. Evaluation is of preventive actions in that they identify problems before they have produced poor quality products. This is why audits are often used as part of the basis for selecting suppliers.
2. What are the differences among the types of inspections offered?
Product inspection is divided into pre-production inspection, during-production inspection, and pre-shipment inspection. Pre-production inspection is to be conducted at the beginning of production or even before the start of manufacturing. During-production inspection is to be conducted when 10%-15% of the production is completed. Pre-shipment inspection takes place when the merchandise is finished, packed and ready for shipment. Based on the outcome of a final inspection, a lot may be accepted, rejected, or placed on hold.
3. What the report will include?
GIS will send the report to the customer 24 hours after inspection. The report will include the result of inspection, on-site check details and related photos. It will show all the inspection details. If you need the sample report, please contact us online.
Quality Management Term
What is ISO?
ISO (the International Organization forStandardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies (ISO memberbodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried outthrough ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject forwhich a technical committee has been established has the right to berepresented on that committee. International organizations, governmental andnon-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISOcollaborates closely with the International Electro technical Commission (IEC)on all matters of electro technical standardization.
What is an inspection?
Activity such as measuring, examining, testing orgauging one or more characteristics of a product or service, and comparing theresults with specified requirements in order to establish whether conformity isachieved for each characteristic
Quality Management term] what is original inspection?
First inspection of a lot according to the provisions of this part of ISO 2859.NOTE This is to be distinguished from the inspection of a lot which has been resubmitted after previous non-acceptance.
What is inspection by attributes?
Inspection whereby either the item is classified simply as conforming or nonconforming with respect to a specified requirement or set of specified requirements, or the number of nonconformities in the item is counted.NOTE Inspection by attributes includes inspection for conformity of items as well as inspection for number of nonconformities per hundred items.
what is item?
Item that which can be individually described andconsidered,EXAMPLES:
a physical item; a defined quantity of material; a service, an activity or a process; an organization or a person; or some combination there of.
Quality Management term] what is nonconformity?
Non-fulfilment of a specified requirement:
NOTE 1 In some situations specified requirementscoincide with customer usage requirements (see defect, 3.1.6). In other Situations they may not coincide, being either moreor less stringent, or the exact relationship between the two is not fully known or understood.
NOTE 2 Nonconformity will generally be classifiedaccording to its degree of seriousness such as:Class A: those nonconformities of a type consideredto be of the highest concern; in acceptance sampling such types of nonconformities will be assigned a very smallacceptance quality limit value;Class B: those nonconformities of a type consideredto have the next lower degree of concern; therefore, these can be assigned a larger acceptance quality limit valuethan those in class A and smaller than in class C, if a third class exists,etc.
NOTE 3 Adding characteristics and classes ofnonconformities will generally affect the overall probability of acceptance of the product.
NOTE 4 The number of classes, the assignment into aclass, and the choice of acceptance quality limit for each class,should be appropriate to the quality requirementsof the specific situation.
What is defect?
Non-fulfillment of an intended usage requirementNOTE 1 The term "defect" is appropriate for use when a quality characteristic of a product or service is evaluated in terms of usage (as contrasted to conformance to specifications).NOTE 2 Since the term "defect" now has definite meaning within the law, it should not be used as a general term.
Quality Management term] what is nonconforming item?Item with one or more nonconformities
NOTE Nonconforming items will generally be classified by their degree of seriousness such as:
Class A: an item which contains one or more nonconformities of class A and may also contain nonconformities of class B and/or class C, etc.;
Class B: an item which contains one or more nonconformities of class B and may also contain nonconformities of class C,etc. but contains no nonconformity of class A.
What is percent nonconforming?
(In A sample) one hundred times the number of nonconforming items in the sample divided by the sample size, via: (d/n)100 where
d: is the number of nonconforming items in the sample;
n: is the sample size
What is responsible authority?
Concept used to maintain the neutrality of this part of ISO 2859 (primarily for specification purposes), irrespective of Whether it is being invoked or applied by the first, second or third partyNOTE 1 the responsible authority may be:
a) The quality department within a supplier's organization (first party);
b) The purchaser or procurement organization (second party);
c) An independent verification or certification authority (third party);
d) any of a), b) or c), differing according to function (see Note 2) as described in a written agreement between two of the parties, for example a document between supplier and purchaser.
What is lot?
Definite amount of some product, material or service, collected togetherNOTE An inspection lot may consist of several batches or parts of batches.
What is the lot size?
Number of items in a lot
What is sample?
Set of one or more items taken from a lot and intended to provide information on the lot.
What is sampling plan?
Combination of sample size(s) to be used and associated lot acceptability criteria
NOTE 1 A single sampling plan is a combination of sample size and acceptance and rejection numbers.
A double sampling plan is a combination of two sample sizes and acceptance and rejection numbers for the first sample and for the combined sample.
NOTE 2 A sampling plan does not contain the rules on how to draw the sample.
Quality Management term] what is normal inspection?Use of a sampling plan with an acceptance criterion that has been devised to secure the producer a high probability of acceptance when the process average of the lot is better than the acceptance quality limitNOTE: Normal inspection is used when there is no reason to suspect that the process average (3.1.25) differs from anacceptable level.
what is tightened inspection?
Use of a sampling plan with an acceptance criterion that is tighter than that for the corresponding plan fornormal inspection
NOTE: Tightened inspection is invoked when the inspection results of a predetermined number of consecutive lots indicate that the process average might be poorer than the AQL
What is the sampling scheme?
Combination of sampling plans with rules for changing from one plan to another
What is a sampling system?
Collection of sampling plans, or of sampling schemes, each with its own rules for changing plans, together with sampling procedures including criteria by which appropriate plans or schemes may be chosen
NOTE this part of ISO 2859 is a sampling system indexed by lot-size ranges, inspection levels and AQLs. A sampling system for LQ plans is given in ISO 2859-2.
Q&A
1. How many goods are required to beready for a pre-shipment inspection?
It depends on the client's requirement. General speaking, pre-shipment inspectionis normally conducted when a shipment is 100% produced and at least 80% packed into export carton.
2. If the client/vendor/factorywould like to change the inspection schedule, what shall they do?
The postponement or cancellation of a previously requested inspection must be made by calling GIS atleast 1 full working day in advance of the inspection date.
3. Will GIS automatically send the inspection report to bothparties or just for the client?
GIS only send inspection report to the client. If anybody need the inspectionreport, we will ask the client for confirmation first.
4. When the inspection report is available?
The official inspection report will be available on the next working day after the inspection finished.
5. Who will pay for the inspection?
Genera lspeaking, the inspection is on the client's account unless we are confirmed bythe client who else will pay for it.
6. When you are required to settle the payment for the inspection?
Any payment is supposed to be done before the inspection.
7. Do GIS work on Saturday and Sunday?
Sunday is normal rest day for GIS. For Saturday, GIS office is closed, however our QCteam will be available.
8. Any extra cost will be generated when the inspection to be done on Sunday?
If the inspection is required to be conducted onSunday, the man-day rate will be multiplied by 1.5 times.
9. How long to apply in advance for any inspection?
To smooth the inspection arrangement and without anydelay, please kindly make your inspection appointments at least 3 working days prior to inspection date you required.
10. May we release the shipment on the basis of the passed inspection report?
Reports of Services are issued on the basis of instructions, information, documents and/or samples provided by the client. GIS inspection report reflects the actual findings as recorded during on-siteinspection; it is not an evidence for shipment. Only the client may make decisionon the shipment.
11. Does GIS open the official invoice for the payment of inspection cost?
GIS will issue the official tax invoice after receipt of your payment.
12. May we pay the inspection cost in RMB, and how about the exchange rate?
Yes, GIS may provide the relevant account for RMB payment, and you may settle the payment with the buying price of the payment day.
13. If the factory may pick your QC up, GIS will not charge travelling cost, right?
Yes, if no traveling cost arising, GIS will not charge relevant cost.
14. May GIS identify the fabric material on site?
Sorry, the fabric material could not be identified on site. If you are concerned, we may help to send sample to any lab for testing. Sure, the lab will charge relevant cost accordingly.
15. If the QC just need half day to finish all the job, may GIS charge 0.5 man-day only?
Sorry, for any inspection, one man-day is the minimum quotation.
16. Does GIS pick up sample and keep in office for each inspection?
It is not a must to pick up sample for each inspection. If it is forbidden, please keep us informed in advance.
17. Any possible to get result right after inspection finished?
GIS may send you draft report at the same day of the inspection finished for your reference. However, the official one will be available in the next working day.
18. As our goods will be ready in the afternoon, any possible to start the inspection by then?
General speaking, we will start our job in the morning in order to smooth the inspection with sufficient working time. Considering special situation, we may negotiate case by case.
19. We need original tax invoice for payment reference. May we get it before the payment to be done?
Sure, just let us know the invoice title and relevant information, and we will issue invoice first for your payment reference.
20. Your QC has found wrong label and mark to be used during inspection. May we ask to stop the inspection as we need to correct all right now?(inspection service)
If the inspection is abortive now, we will charge relevant cost accordingly. Sure, if available, we need contact the client for confirmation first.
21. We have two factories for this big order in same city. Will you charge more cost for two visits in same day?
If they are located in same area within 20mins distance between both, we will not charge more cost for two visit in same day.
22. Our container will be ready at 7:00am, in order to catch the vessel, we could not wait for your QC. May you ask your QC to arrive at our factory at that time?(loading supervision)
If it is a must, we will ask our QC to leave out one day before the loading day, and arrive at your factory as schedule. However, if any change on the loading date, please inform us before our QC leaves, or we will charge abortive cost accordingly.
23. How to calculate your QC's working time?
We will consider two parts for each case, time spent in inspection (inspection time and report-making time) and single traveling from the nearest branch to service location.
24. Who will take on the re-inspection cost?
For the re-inspection fee, GIS will apply to the client, and the client has the right to charge back to its suppliers.
25. Do you require the factory to prepare some goods in advance for your inspection?
No, our QC need select samples by themselves from the bulk in random, then the samples we check may reflect the quality of the bulks.
26. May you issue positive inspection certificate after inspection finished per our L/C requirement?
Yes, but we must get approval from the client for the issue first.
27. If our factory could not provide some equipment for inspection, would you fail the report accordingly?
Yes. Please kindly let us know the situation before the inspection, and, we may check with the client for the issue accordingly.
28. If the factory has doubt on the inspection result, what could they do?
If the factory has doubt on the inspection result, please check with our QC on site. Meanwhile, please call GIS office for further negotiation, and our technical manager will follow up the issue.
29. Per your requirement, 500pcs of goods should be checked during inspection. However, we have not so much blister card for re-packing, any possible to check less?
General speaking, less sampling will lead to uncertain risk. However, we do know what you are concerned. We may check with the client about the situation, and feedback you later.
30. Will GIS put any label on the inspected goods?
Normally, we will put GIS label on the inspected goods or packing for traceability management. However, if it is forbidden, we may pass this procedure. Please let us know any special requirement in advance.
31. GIS normal working days?
Monday to Saturday for inspection division, and Monday to Friday for office.
32. When may the factory apply for a re-inspection after the first inspection failed?
GIS does not have a special timing limit for re-inspection booking. You may ask for a re-inspection anytime when everything is corrected and ready. However, please kindly note bookings received with less than 2 working days' notice may not be completed on schedule.
33. How GIS identify the defects?
The Defects detected during visual inspection are classified within 3 categories, "Critical", "Major" and "Minor" and the normal definitions are:
--Critical Defects: A defect that fails to meet mandatory regulations and/or affects the safety of the consumer when using the product.
--Major Defects: A defect that is likely to result in product failure, reduction the usability of the product and obvious appearance defect affecting the salability of the product.
--Minor Defects: A defect that is not likely to reduce the usability of the product, but is likely to reduce the salability or a discrepancy from the defined quality standard or not same as the original sample
34. What is Acceptable Quality Level (AQL)?
The designated value of defects, expressed as a percentage by the particular sampling procedure and level used will identify what the buyer will normally accept in the majority of cases. Different AQLs may be designed for different defect classifications such as Critical, Major and Minor. Unless specified by the client, GIS will adopt the AQL as follows:
| High valued products | Low valued products | |
| Critical defects | Not allowed | Not allowed |
| Major defects | AQL1.0 / 1.5 | AQL 2.5 |
| Minor defects | AQL 2.5 / 4.0 | AQL 4.0 |
35. We place an order with 24 in 1 ceramic sets in Yangjiang factory. Due to lack of packing material, all of them are not packed, and just put in the factory by pieces. May GIS perform the inspection under this situation?
If it is not urgent, it is better to wait till at least 80% to be packed, then we may select samples by sets. If change the sampling by pieces, it is hard to indentify the defects with the sales units. Sure, we will follow your final instruction accordingly
Inspection Sampling
How does sampling work during an inspection?
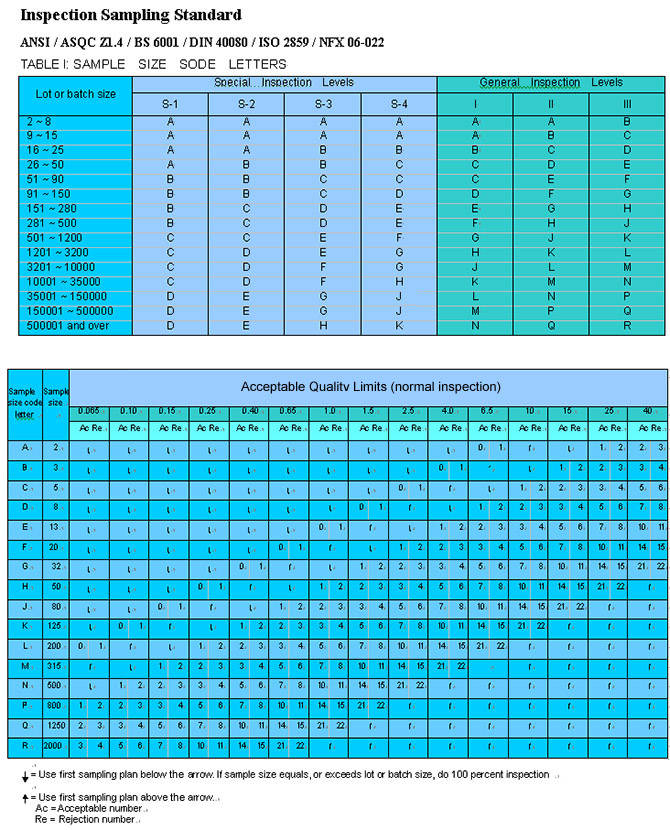
GIS recommends utilizing ANSI Z1.4 2008/ ANSI/ ASQC Z1.4/ BS6001/ DIN 40080/ISO 2859/ NFX 06-022(the same inspection sampling standard showed in ANSI and AQL) for inspection sampling. This standard and its equivalence are designed according to the statistics theory and are indexed with AQL(see next section) . The sampling plans in these standards indicates the number of units of products from each lot or batch which are to be inspected (sample size) and the criteria foe determination of the acceptability of the lot or batch.
Generally, inspection level Ⅱshall be used, otherwise a particular lever which determines the relation between the sample size and the lot or batch size will be prescribed by the responsible authority. Based on the lot or batch size and the inspection level code letters are assigned that cross-reference to the sample size required depending on which plan is being employed. Single and double normal sampling plans are the most commonly used. If you do not have existing sampling requirements, GIS will assist you in determining which plan works best for your specific needs. Samples are checked against a detailed inspection plan for appearance, applicable functionality, packaging integrity, workmanship, etc. If you currently do not have any inspection plan, GIS can assist you. Defects found are classified as critical, major or minor depending on the inspection plans. The acceptable quality limit (AQL) is specified by the responsible authority with the types of defects. A typical set of AQL is described in the section of “What is AQL”. Acceptability of the lot or batch is determined by the corresponding accept/reject criteria with the sampling plan.However, it should be born in mind that this standard is intended to be used on a continuous series of lots, when used without the switching rules, the operating characteristics of the sampling plan must be assessed individually.
What is AQL?
An AQL, or Acceptable Quality Limit, is the quality level that is the worst tolerable process average when a continuing series of lots is submitted for acceptance sampling. The AQL is a parameter of the sampling scheme. It is expected that the product quality lever will less than the AQL. There are normally three AQL specified for critical, major and minor defects separately. A typical set of AQL would be as follows:
| Inspection level | General Level Ⅱ | ||
| Defect | Critical | Major | Minor |
| AQL | 0 | 1.5 | 4.0 |
The smaller the number, the fewer defects will be accepted in the sample of product. When choosing AQLs, it is important that one understands the balance between setting them too low, and rejecting many shipments, and setting them too high and releasing unacceptable product.
Note: AQL formerly was the abbreviation of acceptance quality level and was changed for acceptance quality limit later.
Defectives Classification
Defects is a departure of a quality characteristic from its intended level or state that occurs with a severity sufficient to cause an associated product or service not to satisfy intended normal, or foreseeable usage requirements. It can be classified as:
Critical - A critical defect is on that judgment and experience indicate is likely to:a. result in hazardous or unsafe conditions for individuals using, maintaining, or depending upon the products; b. prevent performance of the tactical function of a major end item.
Major - A major defect is one, other than critical, that is likely to result in failure, or to reduce materially the usability of the unit of product for its intended purpose.
Minor - A minor defect is one that is not likely to reduce materially the usability of the unit of product for its intended purpose, or is a departure from established standards having little bearing on the effective use or operation of the unit of product.

