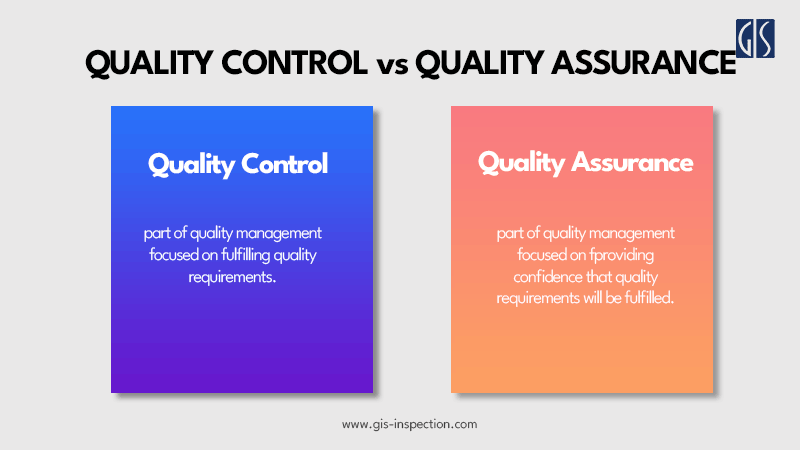
According to ISO 9000:2015 – Quality Management Systems – Fundamentals and Vocabulary, quality control and quality assurance are both part of the QMS. QC focused on fulfilling quality requirements, while QA focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled.
Both Quality Control and Quality Assurance are crucial in customer goods manufacturing industries. Knowing the difference between them is important for creating effective quality management strategies that meet regulations and ensure customer satisfaction.
What is quality control(QC)?
Quality Control can be defined as "part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements." While quality assurance relates to how a process is performed or how a product is made, quality control is more the inspection aspect of quality management. An alternate definition is "the operational techniques and activities used to fulfill requirements for quality."
Quality Control (QC) is a reactive approach that focuses on identifying and rectifying defects in finished products or services. QC involves inspecting, testing, and reviewing outputs to ensure they meet predefined quality standards.
Quality control is the most basic, fundamental quality management activity, and the act of checking finished product to ensure it's up to scratch is often the first thing people imagine when they think of the quality discipline.
Quality control inspections are usually carried out following a comprehensive checklist which guides product checks including specifications, construction, measurements, color and appearance, function, barcodes, labelling and packaging.
Any defects found are classified as either minor, major or critical. The checklist should specify how many defects will be tolerated within each category. For more on this, see our information on Acceptable Quality Limits (AQL).
What is quality assurance(QA)?
Quality Assurance is a clear and concise framework that embraces every element of the operations of an organization, not least quality management which plays an instrumental role in fostering a culture of constant, ongoing improvement. (ISO: Quality assurance: A critical ingredient for organizational success).
ISO 9001:2015 is the most widely recognized international standard used for quality assurance. Other industry-specific standards, like ISO 13485 for medical devices, all derive from the general ISO 9001 quality assurance roadmap.
Different from QC, quality assurance focuses on how a product is made. QA does incorporate elements of quality control, but it is a broad-spectrum process implemented throughout the entire manufacturing process to ensure products are made “right first time”.
Best Practices in Quality Assurance:
- Strategic sourcing and pre-production planning
- Verification of raw materials and manufacturing suppliers
- Product design evaluation
- Comprehensive Risk assessment
- Incoming raw material inspections and laboratory testing
- Systematic product inspections at key production stages
- Certification of products and materials
- Detailed supply chain mapping
- Structured supplier training programs
- Ongoing KPI monitoring and improvement
A quality assurance program would therefore be established to guarantee that outputted products align with those regulatory demands.
Quality assurance also involves corrective action when deviations or errors occur, so that the product is still safe and effective.
Overall, quality assurance requires a combination of planning, testing and monitoring. Companies must develop strategies for meeting quality standards before any product is manufactured.
Testing activities should also be performed during the production process and validated at the end. Finally, monitoring should take place over time to ensure that quality standards are maintained.
While quality control is a reactive function which catches defects or issues in the product before it is shipped, quality assurance is a proactive function which prevents issues from occurring in the first place.
Finally, quality assurance activities typically involve an entire organization (or much of it), while quality control is run by a specific team.
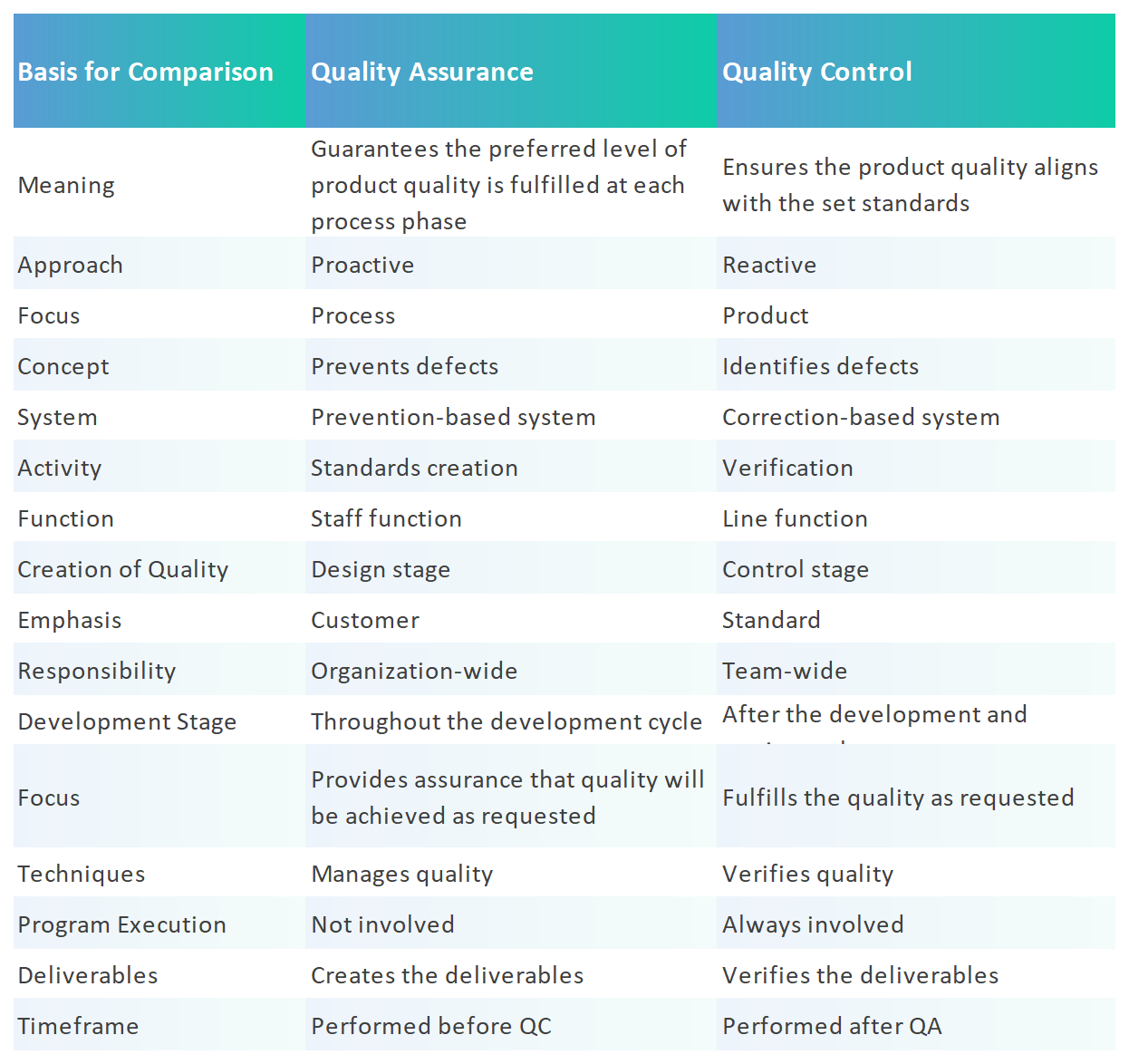
The differences between quality assurance vs quality control
Source: AQS
Quality assurance and quality control are two aspects of quality management. While some quality assurance and quality control activities are interrelated, the two are defined differently.
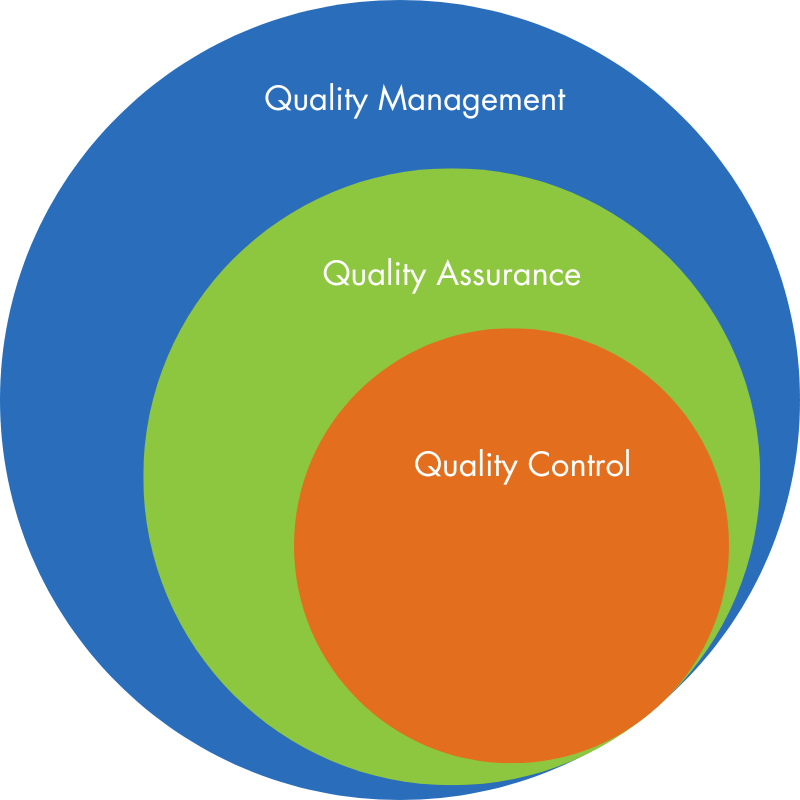
Typically, QA activities and responsibilities cover virtually all of the quality system in one fashion or another, while QC is a subset of the QA activities. Also, elements in the quality system might not be specifically covered by QA/QC activities and responsibilities but may involve QA and QC.
Quality Assurance is focused on improving processes to prevent defects and ensure efficiency, while Quality Control is focused on identifying and fixing defects in finished products or services. QA is proactive, while QC is reactive.
QA, QC, and Inspection
Inspection is the process of measuring, examining, and testing to gauge one or more characteristics of a product or service and the comparison of these with specified requirements to determine conformity.
Products, processes, and various other results can be inspected to make sure that the object coming off a production line, or the service being provided, is correct and meets specifications.
QA and Auditing
Auditing is part of the quality assurance function. It is important to ensure quality because it is used to compare actual conditions with requirements and to report those results to management. An audit is a planned, independent, and documented assessment to determine whether agreed-on requirements are being met.
Common types of audits are of the quality a management system, processes, products, and services. When an audit is to check on conformance to a standard, specifications, contract terms, or regulations it may be called a compliance audit.
GIS Quality Control Services
GIS provides comprehensive quality control and custom quality assurance programs in China and Asia. With more than 20 years of industry experience, our team of expert product inspectors, and auditors help you navigate the complexities of quality management to ensure your products meet requirements.
At GIS, we understand that every product category and every factory is unique. That’s why we tailor our inspection protocols, testing plans, and audit programs to match your risk profile, quality expectations, and production timelines.
Whether you’re sourcing from a new supplier, managing multiple factories, or scaling your business globally, our experts act as your on-the-ground quality partner.
Our services include:
Pre-production inspections (PPI)
to verify materials, components, and early-stage planning
During-production inspections (DPI)
to reduce defects and keep your mass production on track
Pre-shipment inspections (PSI)
for final confirmation of quantity, workmanship, safety, and compliance
Container loading checks (CLC)
to ensure correct products, packaging, and safe loading
Supplier audits
factory capability, social compliance, environmental audits
Customized QA programs
designed to prevent defects, reduce risk, and optimize supplier performance
We have developed smart solutions to support you in quality control and supply chain management. Contact us today to discuss your quality needs and discover how we can support your business growth!
Inspect by GIS Inspection
General Inspection Service-GIS is an international third-party quality control inspection company headquartered in China in 2005, which provides a professional range of product quality inspection and factory audit services to clients across multiple industries. We have set up an inspection network covering China, Vietnam, India and Malaysia. By employing only full-time inspectors, GIS is trusted by more than 12,000 brands globally.