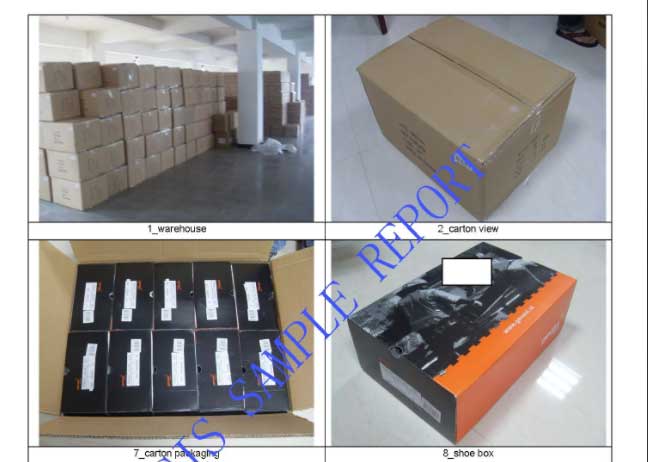
Footwear manufacturing always uses a wide range of materials and requires several different production processes which makes footwear quality control a highly demanding and specialized process.
Whether you’re manufacturing athletic shoes, dress shoes, sandals, boots, safety shoes, and children's shoes, footwear inspection is essential that can ensure your suppliers are meeting your quality and safety expectations, which not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens brand reputation.
This article discovers the essential checklists when processing a pre-shipment quality inspection for shoes and the most common defects that occur in the manufacture, storage and usage of footwear.
Essential Checklists for Footwear Pre-shipment Inspection
Quality control in the footwear industry involves a series of inspections and checks designed to identify and rectify defects at various stages of production. These inspections help to prevent substandard products from reaching consumers, which can lead to returns, complaints, and ultimately, a damaged brand image.
Implementing a detailed and thorough footwear inspection checklist is essential for maintaining high standards. Below, we outline a common checklist on pre-shipment inspection for shoes.
1. Quantity Verification
Accurate quantity verification prevents logistical issues and ensures that the client receives the correct number of products.

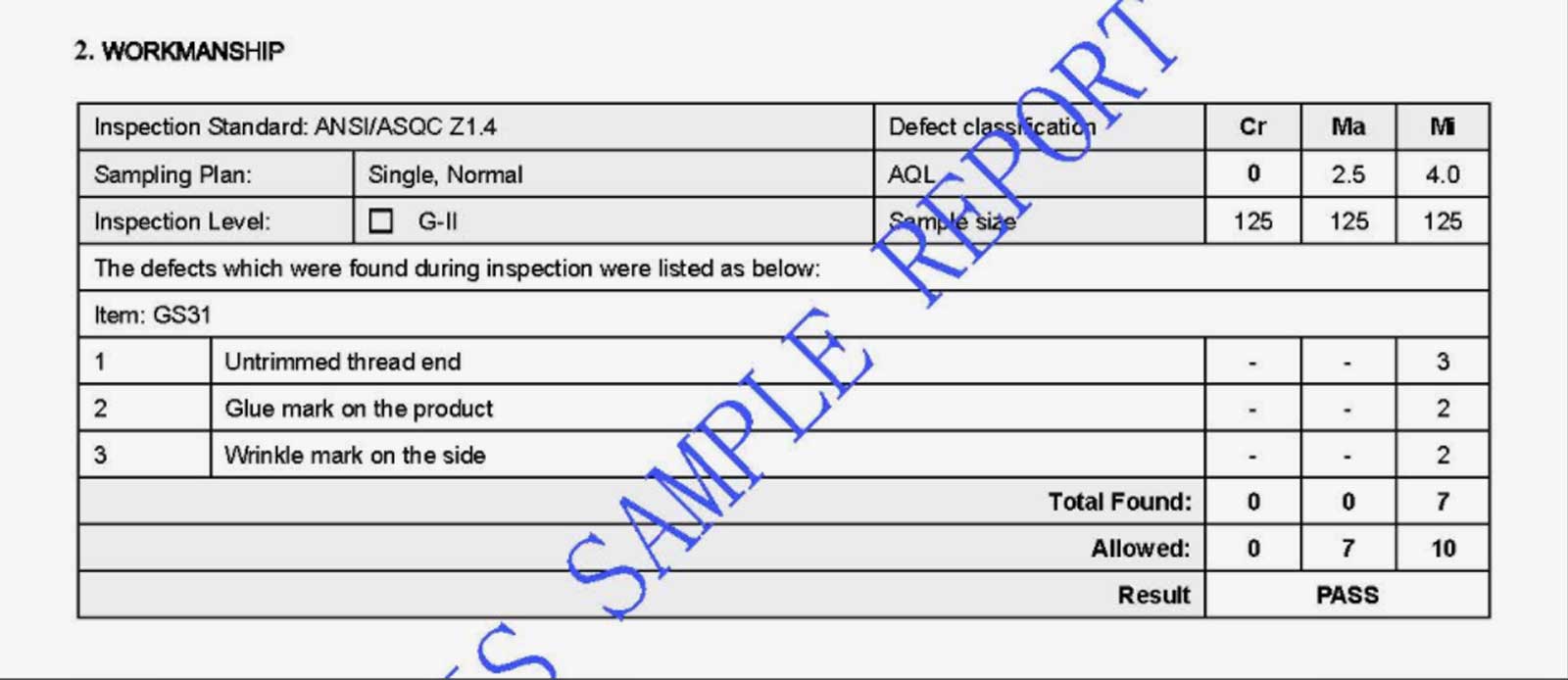
2. workmanship check
A comprehensive workmanship review ensures that the final product meets the highest standards of quality and craftsmanship.
3. Packaging Inspection
Proper packaging and labeling protect the product and provide necessary information to retailers and consumers.
4. Product Style and Construction Verification
Ensuring conformity with design and construction standards is critical for maintaining brand integrity and customer satisfaction.

5. Functional and Performance Tests for Footwear
- Carton drop test: With reference to ISTA 1A drop test method. The package or product should not be damaged. after the test
- Assortment check: The packing assortment should be correct as client's requirement and package marking
- Color shade check: No color shade within same pair is allowed; The color shade in the whole shipment with grey scale 4 is allowed for dark color, with grey scale 4-5 is allowed for light color.
- Function check: The functional components should run smoothly without jam or any malfunction issue.
- Reliability test for Zipper/button/snap or any other functional component: Open and close the tested component back and forth 20 times, the component should be remained good as it's after the test.
- Product size / weight measurement: According to product spec or approved sample. Apply +/- 3% if no detail tolerance issued or requirement from client.
- Fitting check: The shoes should be fit the intended model feet or person feet well.
- Barcode scan check: The barcode must be scannable and with the correct number.
- Metal detection for shoes have sewn process: No broken needle or metal should be detected.
- Odor and mildew check: Should not have irritative odor and Mildew.
Check a footwear quality control inspection report!
Quality Defects during Visual Inspection in Footwear
When purchasing shoes, quality is a key factor that determines comfort, durability, and overall value. Whether you are a retailer, buyer or manufacturer, preventing defects at footwear through quality inspection is key to ensure satisfaction of consumers.
Following are the most common defects that occur in the manufacture, storage and usage of footwear and that can be determined during visual inspection of the end product.
1. Common Defects for Footwear Inspection

- Colour variation: Obvious difference in colour that can be seen in the same area within a pair, or in one component part or in theadjacent areas of one item of footwear.
- Damaged shoe: Footwear that has changed in appearance due to careless operation that adversely affects its performance.
- Inconformity with the design: Situation when a product does not conform to the reference sample or drawing which both parties have agreed upon.
- Mildewing: Infecting process by microorganisms on material at any part of the footwear.
- Non-compliant box: Shoe box that does not conform with the footwear inside.
- Poor printing: Printing on footwear that is incomplete or unclear.
- Soiled shoe: Shoe with dirt or adhesive mark on the upper, lining or sides of the sole due to careless handling or cleaning.
- Spue: White frost-like layer that appears on the surface of footwear.
- Weave fault: Defect that reduces the expected performance of the fabric
2. Materials Defects for Footwear Inspection
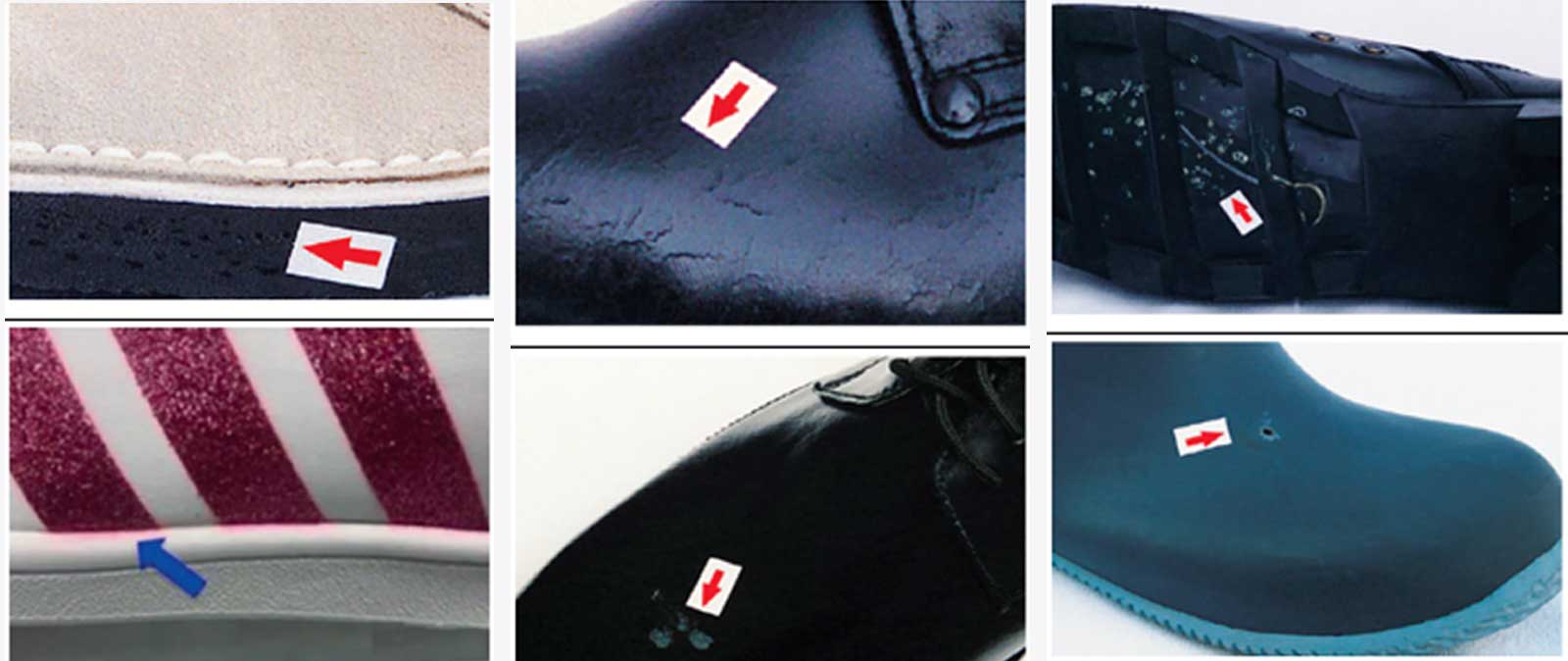

- Air hole: Small hole which develops in the colloid structure of materials.
- Colour migration: Discolouration caused by movement of colour from one material to another
- Crazing: Cracks in the coating of upper materials.
- Discolouration: Staining or fading of the original material colour, either in discrete areas or across the whole product.
- Impurity: Small particles that do not belong to the original formulation and show on the material.
- Pit: Small hole in the surface of footwear
- Shade variation: Differences within materials that cause a difference in the shade of the finished footwear.
- Sulfur blooming: Yellow or white layer that appears on the surface of rubber materials.
3. Components Defects for Footwear Inspection
Defects in upper
- Broken folding: folding of upper over the edge that has broken during the making or wearing process.
- Crease on the upper: wrinkles on the upper area of footwear due to poor sewing process.
- Delamination of upper: Separation of upper into its constituent layers, either in whole or in part.
- Exposed lasting margin: Scoured lasting margin of the upper that is exposed above the lasting edge.
- Grain crack: Grain surface of leather in upper that is split or cracked, or on which a rupture pattern has developed.
- Wrinkled leather/loose grain: Grain whose attachment to corium has been eroded, giving rise to pronounced wrinkles when leather is bent, grain inside.
Defects in counter and toe puff
Collapsed counter: counter area of footwear that has collapsed due to the stiffener either becoming detached or weakened.
- Collapsed toe puff: toe that is distorted and buckled because the reinforcement has collapsed within, leaving creases and/or dents
- Uneven counter: counter edge that has become creased
- Uneven toe puff: toe puff of the shoe that has become creased
Defects in Lining and insock
- Crease/wrinkle: permanent hard folding mark that appears in the middle of lining or insock
- Broken insock: textile on insock component that has torn during the placement or wearing process
- Separated lining: lining that has separated from the upper, leaving gaps or open areas
- Uneven lining: lining that has wrinkled or creased
- Uneven lining edge: edge of lining that is crooked
Defects in welt and foxing
- Broken foxing: foxing that has cracked
- Foxing curling: departure of foxing from physical flatness with the tendency to curve into a cylindrical shape
- Poor foxing positioning: foxing that is too high, revealing the outsole
- Uneven welt: welt surface that is uneven or welt edge that is crooked or notched
- Insufficient welt: welt that fails to cover the circle of the lower outer edge of footwear
Defects in heel
- Creased heel cover: heel coating that is wrinkled, not fixed tightly or not fully stretched
- Se heel: heel that has not been securely fastened causing it to work loose easily or come off altogether
- Loose top piece: top piece that has not been securely fastened to the heel, causing it to work loose easily or come off altogether
- Slanted heel: heel that does not sit on the ground flat but leans with the top piece resting on its edge
- Uneven top piece: top piece surface that is distorted
Defects in outsole
- Blister: soft area that presents an irregular surface or protuberance without a break on the surface
- Deformed outsole: outsole profile that is distorted
- Mould spew: material which has flowed into the mould gap and remains on the surface
- Moulding defect: structure that is incomplete or deformed
Defects in other components
- Fective lace: lace containing one or more defects which could affect its functionality,
- Defective touch and close fastener: touch and close fastener containing one or more defects which could affect its functionality,
- Defective zipper: zipper containing one or more defects which could affect its functionality,
- Eyelet clenching fault: eyelet edge which is sticking out,
- Loose ornaments: ornament not securely attached to the shoe due to poor bonding force,
- Rusty accessory: metal accessory with a corrosive substance which is formed by the action of water and air,
4. Manufacturing defects for Footwear Inspection
Defects in assembly
- Insufficient insock: insock that is too short to cover the heel area and sides of the insole,
- Mismatching upper and sole: footwear with an upper whose size does not match with the sole size,
- Misplaced heel: heel that does not sit correctly on the seat of the footwear,
- Under-seated heel: heel whose top is smaller than the area of the seat,
Gluing defects
- Adhesion failure: detachment of two parts connected with adhesive material,
- Glue overflow: excessive amount of adhesive that has bled from the adhesion part to the surface,
- Insufficient gluing: insufficient application of glue to components, causing their detachment
- Trace of glue: glue stains on the insock or upper of the finished footwear.
Sewing defects
- Broken stitching/thread breakage: thread that has broken altogether, perhaps as a result of poor thread quality or poor tension in the stitching process.
- Crooked stitching/non-parallel stitches: disordered or crooked alignment between the stitch line and the intended edge on an upper.
- Flipped thread: under thread and top thread that have switched places, causing the under thread to float on the upper surface.
- Merged stitching: stitch threads that overlap in some areas of a shoe.
- Skewed back seam: back seam that is not located in the line of heel symmetry.
- Skipped stitching: thread that is skipped, leading to the thread coming away from the upper in a loop alternating with stitches on both sides.
- Uneven lapping: upper material with a rough or/and uneven overlap.
Defects in other process
- Extruded nail: nail which is used to fasten some components of footwear through the insole.
- Poor lasting: insufficient lasting that results in wrinkles due to poor process technique or the incompatibility of the upper and the last.
- Remaining staple: staple, used for positioning during lasting, that has been left in the insole.
- Uneven nail: nail applied to fix a heel or top piece that is unevenly distributed.
- Uneven top facing: top line that varies in size.
5. Defects within pairs for Footwear Inspection
- Different apron size: size of central portion on the top of the vamp that is variable within pairs.
- Ornament difference: difference between ornaments in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Pair colour variation: obvious difference in colour that can be seen in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Pair grain variation: different crudeness in grain of leather in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Pair nap variation: different roughness in nap of leather in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Pair toe puff variation: different shape or size of toe puff in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Pair vamp variation: different shape or size of vamp in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Pttern difference: different pattern in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Toe spring variation: obvious difference in the distance between the ground level and the bottom surface of the sole at the toe between two items in a pair.
- Vamp length deviation: different dimensional length of vamp in the same area of two items in a pair.
- Variable quarter height: quarter height that is variable and/or not comparable between two items in a pair.
6. Marking Defects for Footwear Inspection
- Missing environmental claim: absence of relevant labels on products which claim to have environmentally friendly aspect(s).
- Illegible barcode: unclear barcode marking on a box or carton.
- Illegible sizing: unclear size marking on footwear.
- Nonconforming pictogram: pictogram which does not comply with a regulation, law or standard.
- Missing label: label that is absent from the footwear and/or box during inspection.
- Missing pictogram: pictogram that is absent from the finished footwear during inspection.
- Poor mark: mark on the footwear that is illegible and deformed.
- Missing safety mark: safety marking that is absent for footwear during inspection.
- Missing shipping mark: shipping mark that is absent on carton during inspection.
Learn more: ISO 20537:2025(en) Footwear — Identification of defects during visual inspection — Vocabulary
GIS Third-Party Footwear Inspection Service
General Inspection Service is the top third-party quality control company in China. With over 20 years of experience in conducting inspections, GIS Inspection has developed extensive expertise in footwear quality control. Our extensive experience has allowed us to consistently identify several recurring defects during our footwear inspections.
Partnering with a third-party inspection like GIS Inspection, enables you to identify and control quality concerns at the source.
Contact our footwear quality assurance experts to customize your inspection requirements and receive within 24 hours of our detailed inspection reports that you can see images of any defects found as if you’re in the factory check the shoed yourself.
Inspect by GIS Inspection
General Inspection Service-GIS is an international third-party quality control inspection company headquartered in China in 2005, which provides a professional range of product quality inspection and factory audit services to clients across multiple industries. We have set up an inspection network covering China, Vietnam, India and Malaysia. By employing only full-time inspectors, GIS is trusted by more than 12,000 brands globally.



